Dealing with head lice can be a frustrating experience, but understanding their lifecycle can empower us to tackle infestations more effectively. This guide offers an expanded look into the life stages of head lice, alongside more detailed prevention and treatment strategies.
Introduction to Head Lice
Head lice are tiny parasites that are found on the human scalp. They feed on small amounts of blood drawn from the scalp and are a common issue, particularly among children.
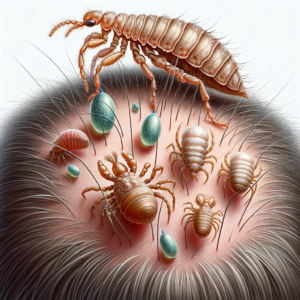
Detailed Lifecycle Stages
- Egg (Nit) Stage:
- Location and Identification: Nits are most commonly found around the ears and near the neckline. They are securely glued to hair shafts and do not fall off easily, unlike dandruff.
- Hatching Process: Within 6-9 days, a nymph emerges. The warmth and humidity of the scalp are crucial for the hatching process.
- Nymph Stage:
- Physical Development: Nymphs resemble adult lice but are smaller. They mature after three molts and reach adulthood about 9-12 days after hatching.
- Feeding Habits: Nymphs need to feed on blood for survival and development. They start feeding almost immediately after they hatch.
- Adult Louse:
- Lifespan and Reproduction: Adult lice can live up to 30 days on a person’s scalp. A female louse is larger than a male and can lay about 6 eggs per day.
- Mobility: Adult lice can crawl quickly but cannot jump or fly, which is a common misconception.
Advanced Prevention Strategies
- Environmental Control: While lice do not survive long without a human host, cleaning items that came in contact with the infested person (like bedding and hairbrushes) is important.
- Community Awareness: Informing schools and communities about an outbreak can help prevent the spread.
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches
- Manual Removal: Using a fine-toothed comb to remove lice and nits is effective but time-consuming. It’s often used in conjunction with other treatments.
- Chemical Treatments: Over-the-counter and prescription shampoos and lotions are available. It’s vital to follow the instructions to avoid resistance development.
- Natural Remedies: Some prefer natural methods like essential oils, but their effectiveness is not scientifically proven.
- Professional Services: Professional lice removal services are available and can be a convenient option.
Myths and Misunderstandings
- Myth: Having head lice means you are unclean.
- Fact: Lice infestation is not related to cleanliness and can affect anyone.
- Myth: Lice can transmit diseases.
- Fact: Head lice are not known to spread disease.
Conclusion
Understanding the lifecycle and habits of head lice is key to effectively managing an infestation. With proper treatment and preventive measures, lice can be controlled and eliminated. Remember, while inconvenient, lice infestations are a common part of human life and can be dealt with effectively. If you find yourself with head lice or are unsure if you have an infestation, reach out to our specialists today for a professional review!

Recent Comments